Cancer is a disease that has several manifestations and it is primarily associated with abnormal cell groups. These cancer cells continue to divide and grow to produce tumors. Among all types of cancer, lung cancer is the most life-threatening disease all over the world.
According to the World Health Organization, lung cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide. In 2008, 1.37 million deaths caused by lung cancer occurred throughout the world. Available data shows that lung cancer is the largest among new cancer diagnoses worldwide (1,350,000 new cases and 12.4% of total new cancer cases) and it is the largest cause of death from cancer globally (1,180,000 deaths and 17.6% of total cancer deaths).
It is the most common cancer in men worldwide (1.1 million cases, 16.5% of the total). Among females, it was the fourth (516,000 cases, 8.5% of all cancers) most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second (427,000 deaths, 12.8% of the total) leading cause of cancer death. A report by National Cancer Centre Singapore has shown that 1.2 million people were diagnosed with cancer and 7700 people died of cancer on average in the year 2015 and 158,080 cases were expected by the end of 2016. In Brazil, an average of 28,220 cases found in 2016 with 17,330 males and 10,890 females.
Abstract
This paper presents a systematic review of the literature focused on the lung nodule detection in chest computed tomography (CT) images. Manual detection of lung nodules by the radiologist is a sequential and time-consuming process. The detection is subjective and depends on the radiologist’s experiences. Owing to the variation in shapes and appearances of a lung nodule, it is very difficult to identify the proper location of the nodule from a huge number of slices generated by the CT scanner. Small nodules (< 10 mm in diameter) may be missed by this manual detection process.
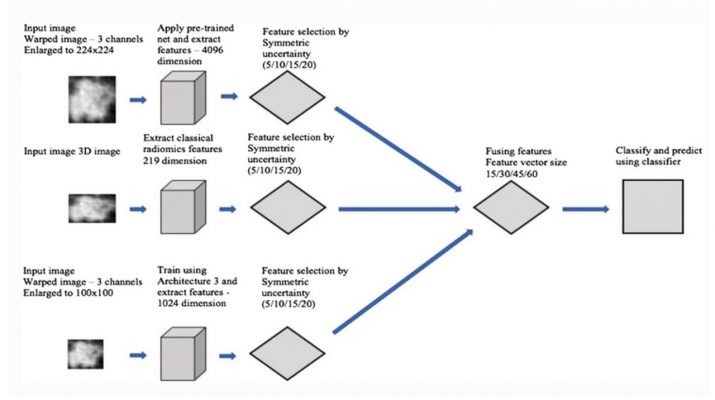
Therefore, computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system acts as a “second opinion” for the radiologists, by making the final decision quickly with higher accuracy and greater confidence. The goal of this survey work is to present the current state of the artworks and their progress towards lung nodule detection to the researchers and readers in this domain. This review paper has covered the published works from 2009 to April 2018. Different nodule detection approaches are described elaborately in this work. Recently, it is observed that deep learning (DL)-based approaches are applied extensively for nodule detection and characterization. Therefore, the emphasis has been given to the convolutional neural network (CNN)-based DL approaches by describing different CNN-based networks.
Amitava Halder, Debangshu Dey & Anup K. Sadhu